Calorimeter Showers Classifier
Late 2024 — Physics ML: Electrons vs Hadrons
About
Building a binary classifier from scratch to distinguish electron showers (signal) from hadron showers (background) in electromagnetic calorimeters at CERN's LHC. Features: shower depth and width.
View on GitHub →Physics Background
At CERN's LHC (ATLAS, CMS), electromagnetic calorimeters measure energy from incoming particles. Electron showers have different depth and width characteristics than hadron showers — we exploit this to classify them.
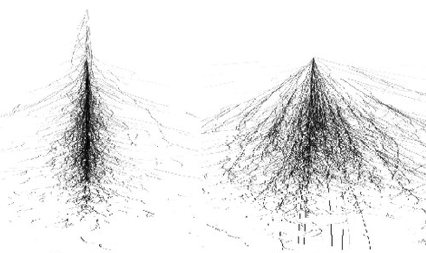
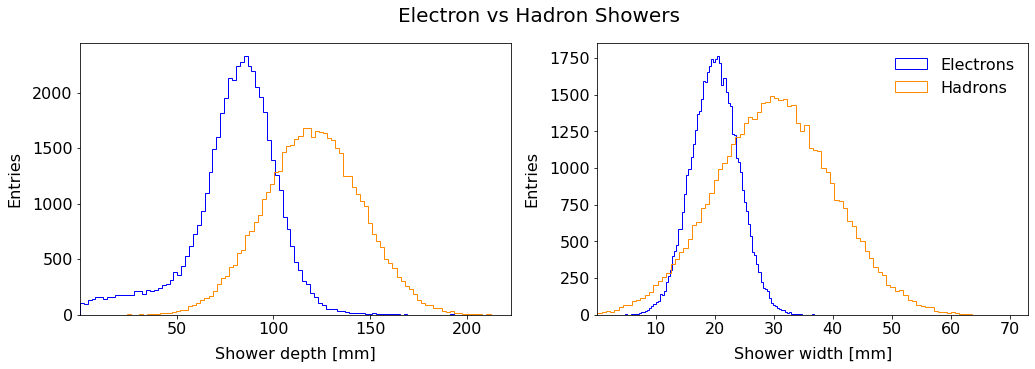
Implementation Steps
1. Feature Scaling
Standardize features to zero mean and unit variance for better gradient descent
2. Core Functions
Sigmoid hypothesis, cross-entropy loss, gradient computation
3. Training
Gradient descent optimization with Adam optimizer
4. Evaluation
Accuracy, Recall metrics on test set
Results
Data Scatter Plot
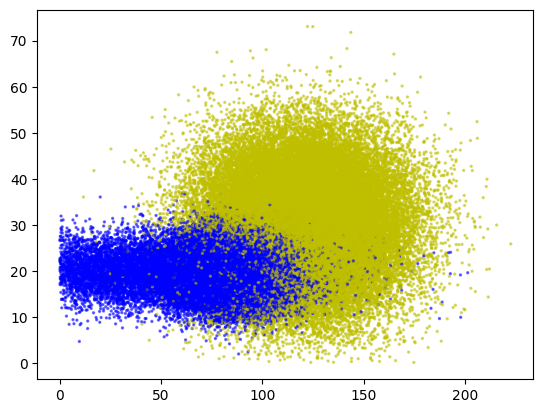
Scaled shower depth vs width
Training Progress
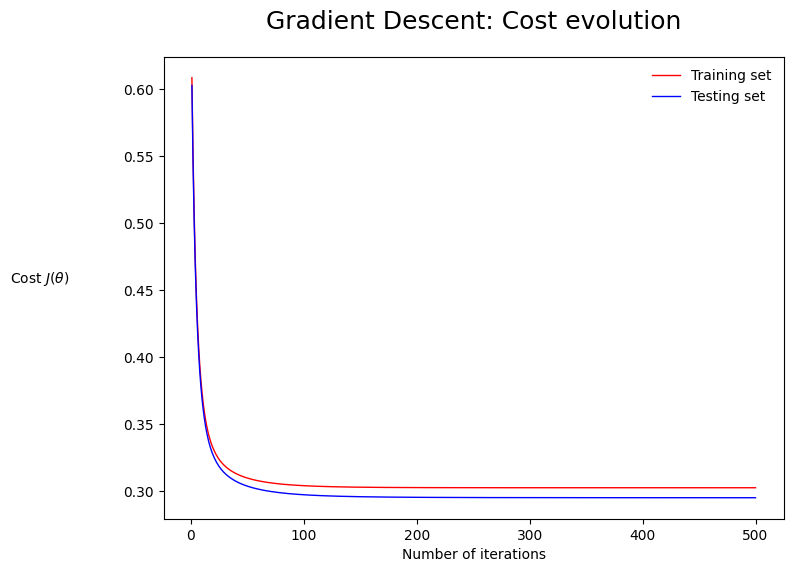
Cost vs epochs — smooth convergence
Decision Boundary
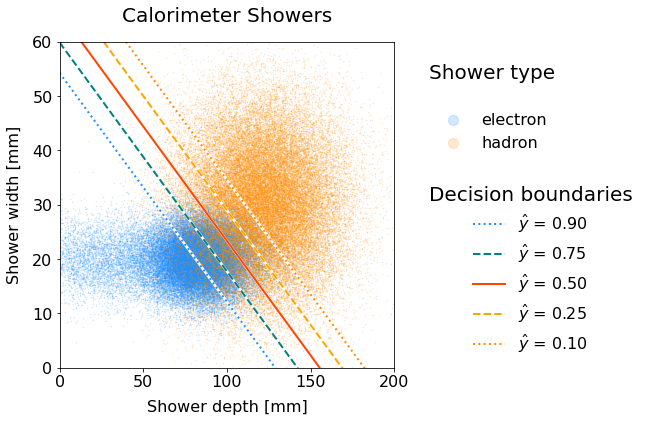
Linear boundary separating electrons from hadrons
Key Takeaways
- ✅ Physics intuition — electrons and hadrons have different shower profiles
- ✅ Feature scaling is critical for gradient descent efficiency
- ✅ Logistic regression can solve real physics classification problems
- ✅ From-scratch implementation deepens understanding of ML fundamentals