🖼️
AIMS Coursework
Image Denoising Autoencoder
Late 2024 — Fully Convolutional Network for Noise Removal
Autoencoder
Denoising
FCN
LFWcrop
About
A fully convolutional autoencoder that removes Gaussian noise from face images. Trained on the LFWcrop dataset (64×64 color images), the network learns to reconstruct clean images from noisy inputs.
View on GitHub →Network Architecture
Encoder
- • 4 convolutional layers with ReLU
- • 3 average pooling layers
- • Input: (3, 64, 64) → Output: (32, 8, 8)
Decoder
- • 4 transposed convolutional layers
- • Restores spatial dimensions
- • Input: (32, 8, 8) → Output: (3, 64, 64)
Training Details:
Loss: MSE
Optimizer: Adam
LR: 0.001
Epochs: 50
Results
0.0014
MSE (batch)
0.0015
MSE (full test set)
Training & Validation Loss
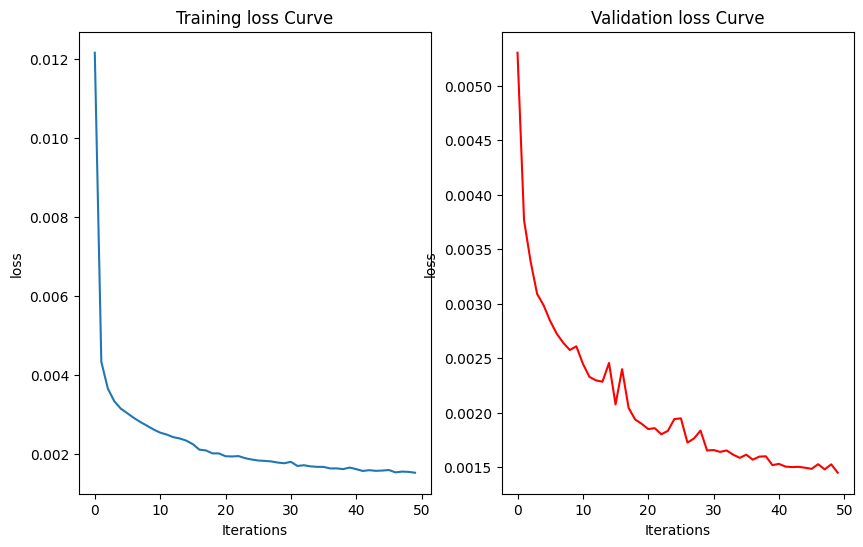
Smooth convergence over 50 epochs
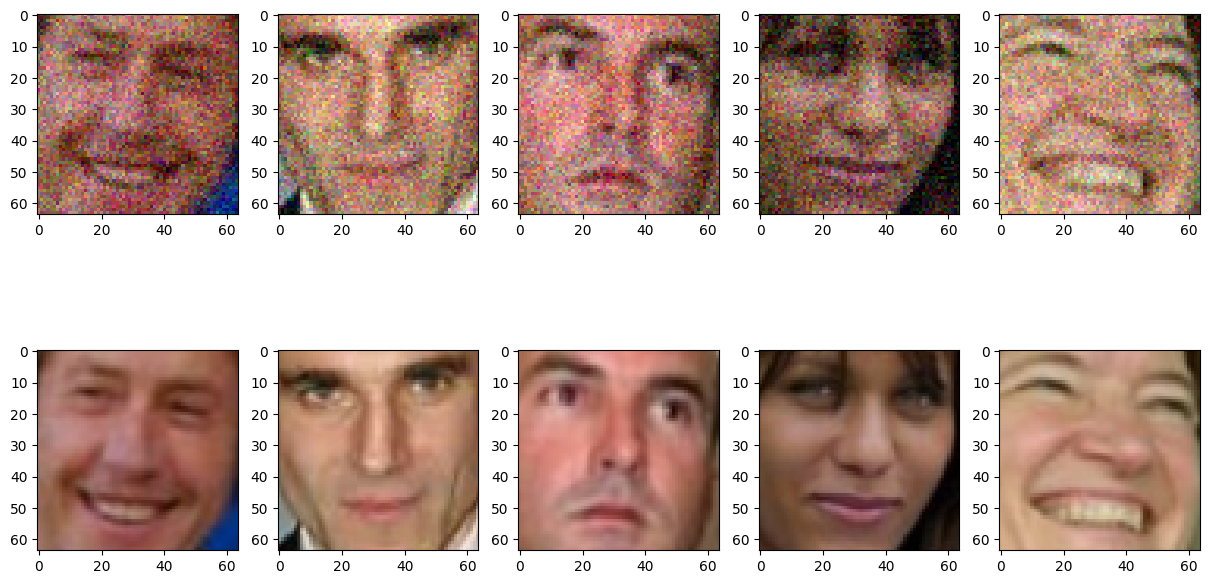
Qualitative Results: Noisy → Denoised

Top row: noisy inputs | Bottom row: denoised reconstructions
Example: Noisy vs Clean Training Data
Discussion
- • Model effectively removes noise but sometimes produces slightly blurry reconstructions
- • Given the low quality of original LFWcrop images, results are impressive
- • Blurring occurs due to MSE loss smoothing pixel values
Key Takeaways
- ✅ Autoencoders work well for image denoising tasks
- ✅ Fully convolutional architecture preserves spatial information
- ✅ MSE loss achieves good quantitative results but can cause blurring
- ✅ Future work: UNet architecture, perceptual loss, other noise types