📉
AIMS Coursework
Overtraining Analysis
Late 2024 — Decision Stumps, Trees, and Overfitting
Decision Trees
Random Forest
Gini Index
Overfitting
About
Exploring binary classification with decision stumps and trees, focusing on overtraining tendencies and generalization capabilities. Includes Gini index calculations, optimal threshold determination, and comparing Decision Tree vs Random Forest with different hyperparameters.
View on GitHub →Methodology
Dataset
Physics data with features: Δηjj (detajj) and mjj (massjj) for binary classification of signal vs background.
Decision Stump
- • Gini index calculation
- • Optimal threshold: 220 GeV (massjj)
- • Minimizes cost/impurity
Overtraining Check
- • Compare train vs test distributions
- • Decision Tree (max_depth=2)
- • Random Forest (100 estimators)
Results
Decision Stump Cut
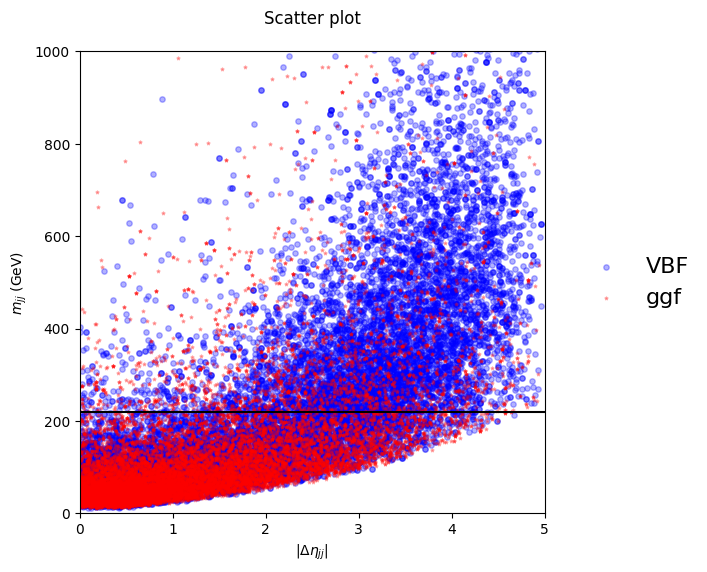
Optimal threshold at 220 GeV separates signal and background
Decision Tree (max_depth=2) — Good Generalization
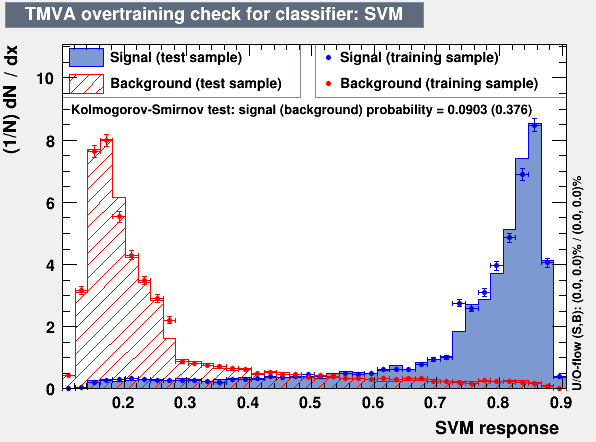
Train and test distributions overlap well — minimal overfitting
Random Forest (Default) — Overfits!
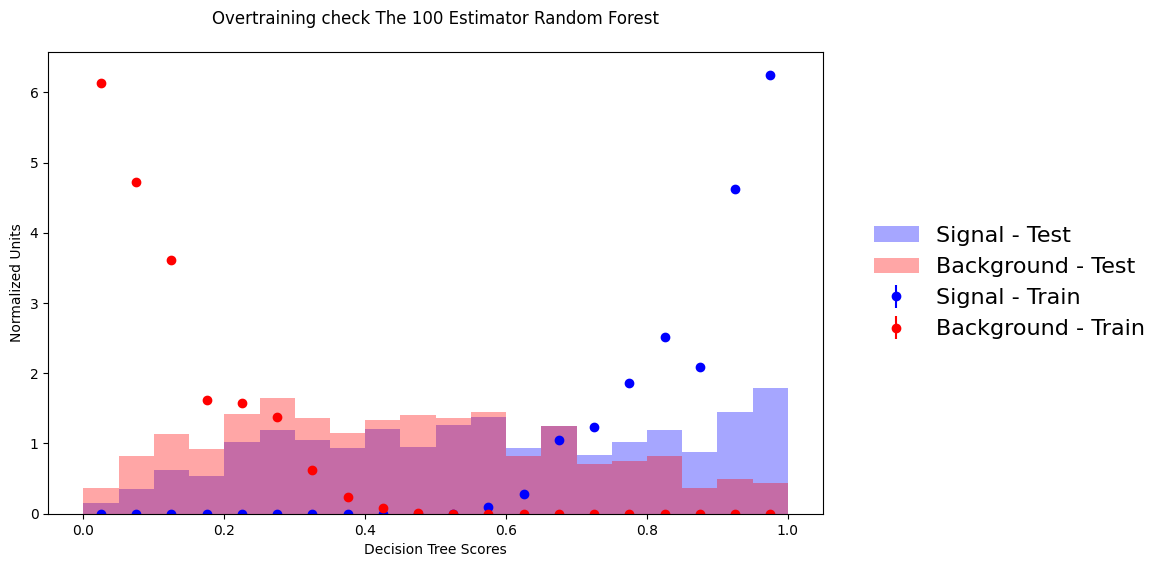
Severe overfitting — train/test mismatch
Random Forest (max_leaf=32) — Fixed!
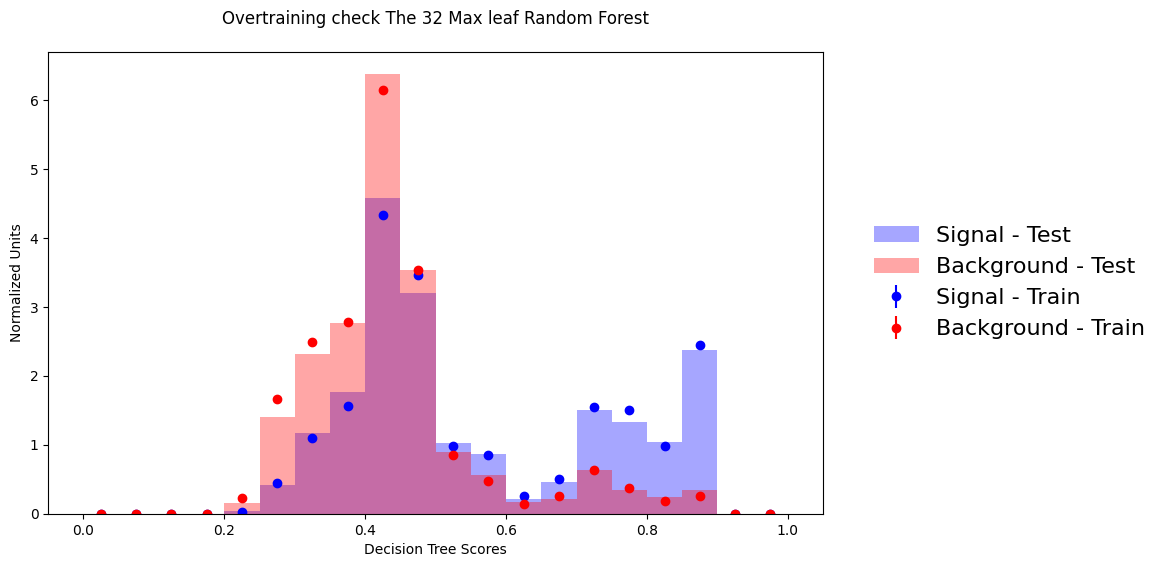
Constrained complexity reduces overfitting
Key Takeaways
- ✅ Decision stumps work well for simple feature separation
- ✅ Overtraining check crucial — compare train vs test distributions
- ✅ Random Forest can severely overfit without constraints
- ✅ Hyperparameter tuning (max_leaf_nodes) prevents overfitting