Transfer Learning & Saliency Maps
Late 2024 — VGG16, MobileNet, and Model Interpretability
About
Training CIFAR-10 classifiers using pre-trained models (VGG16, MobileNetV2, MobileNetV3-Large) and investigating what the model "sees" using saliency maps generated through masked image techniques.
View on GitHub →Transfer Learning Comparison
Pre-trained models on ImageNet (224×224) adapted for CIFAR-10 (32×32). All convolutional layers frozen, only classifier replaced.
| Model | Test Accuracy | Val Loss | Training Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| VGG16 | 67.60% | 0.9409 | Very slow |
| MobileNetV2 | 78.71% | 0.6159 | ~1064s |
| MobileNetV3-Large ⭐ | 84.37% | 0.4642 | ~1019s |
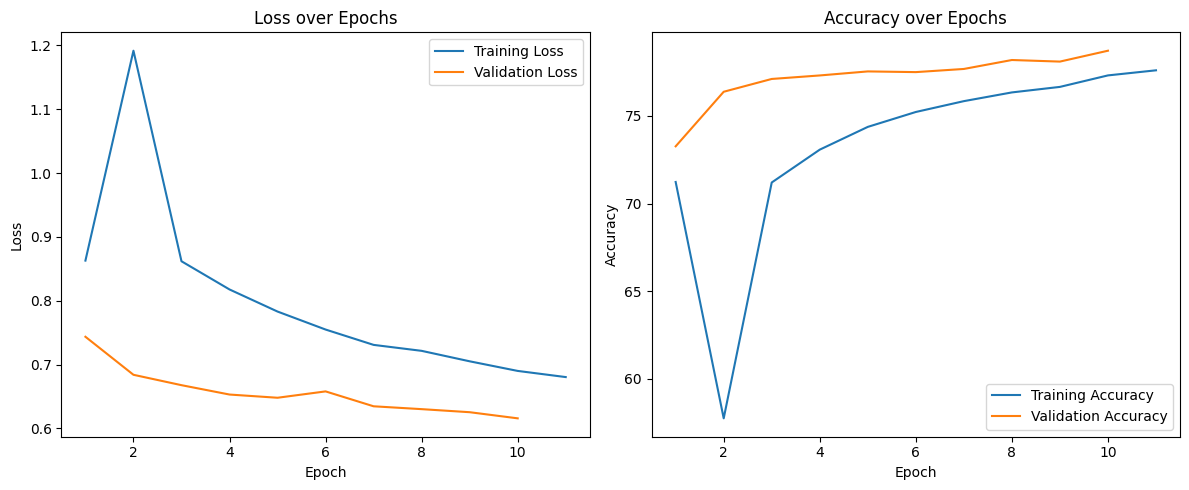
MobileNetV2 training curves
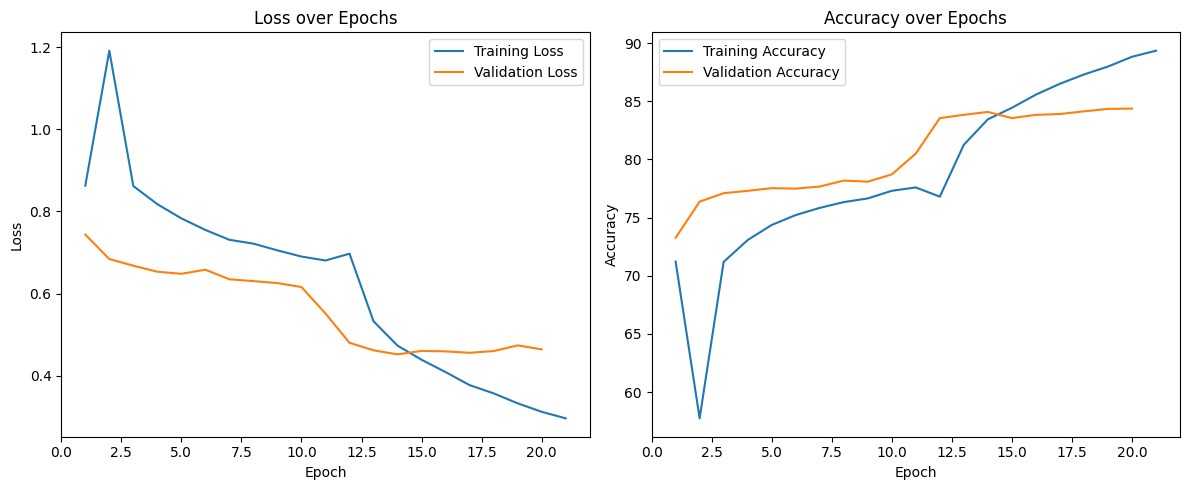
MobileNetV3-Large training curves
Saliency Map Generation
Understanding what the model "sees" by sliding a black mask across the image and measuring the drop in classification probability. Regions where masking causes the biggest probability drop are most important to the model.
Procedure:
- Apply a 30×30 black mask sliding across the image (stride 20)
- Pass each masked image through the model
- Record classification probability for the correct class
- Reshape into 2D heatmap showing region importance
Original Image

Input: French horn and musicians
Saliency Map
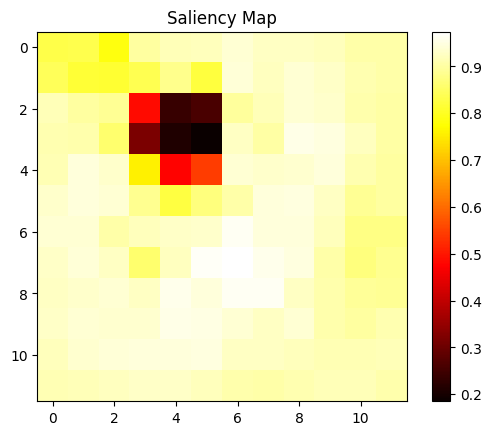
Model focuses on the French horn region
Insight: The saliency map clearly highlights the French horn as the critical region for classification. When the mask overlaps significant object regions, prediction probability drops significantly.
Key Takeaways
- ✅ MobileNetV3-Large wins — best accuracy (84.37%) with efficient training
- ✅ Transfer learning works even with resolution mismatch (224×224 → 32×32)
- ✅ Saliency maps provide intuitive model interpretability
- ✅ Smaller efficient models (MobileNet) can outperform larger ones (VGG16)