🎨
Computer Graphics
2024 — C++ and OpenGL Fundamentals
About
Learning computer graphics from the ground up with C++ and OpenGL/GLUT. From basic 2D shapes to 3D transformations, exploring the mathematics that powers visual computing.
🖼️ Rendered Examples
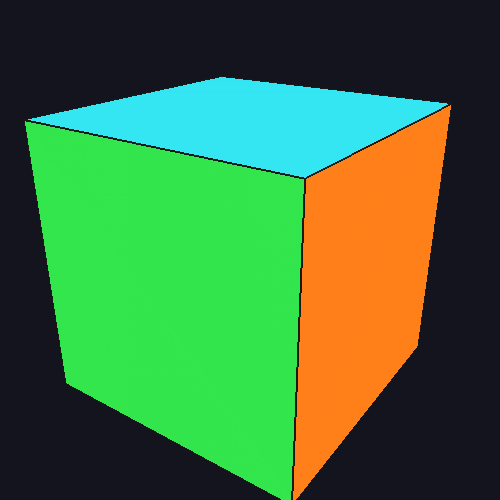
3D Colored Cube
Depth buffering, perspective projection, edge rendering, and per-face coloring
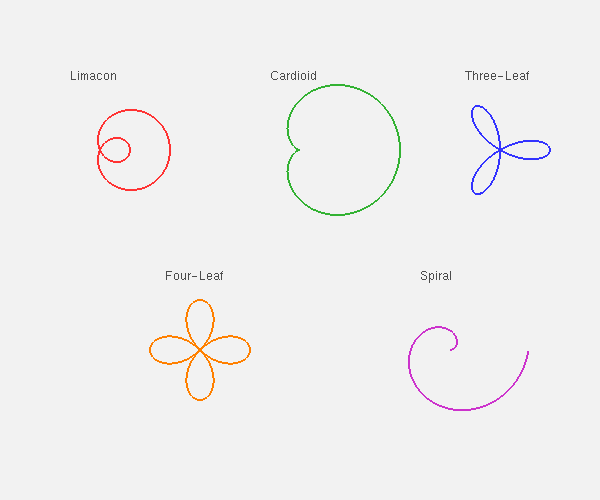
Mathematical Curves
Limacon, Cardioid, Three-Leaf, Four-Leaf, and Spiral using polar equations
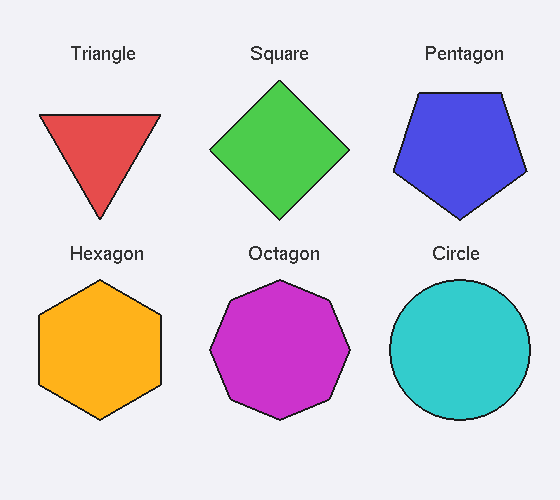
Regular Polygons
From triangle to circle — filled shapes with outlines
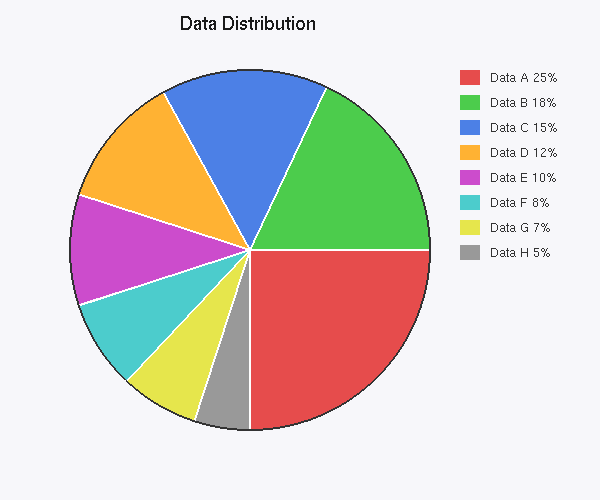
Data Visualization
Pie chart with dynamic slices, labels, and legend
Topics Covered
📐 2D Graphics
- • Basic shapes: lines, triangles, polygons
- • Mathematical curves (polar coordinates)
- • Transformations: translate, rotate, scale
- • Filled polygons with vertex colors
🧊 3D Graphics
- • 3D primitives: cubes, spheres
- • Perspective and orthographic projection
- • Depth buffering (Z-buffer)
- • Model-View-Projection matrices
🎨 Advanced Topics
- • Bezier curves and surfaces
- • Filled hexagons and complex polygons
- • Animation with timer callbacks
- • Double buffering for smooth rendering
📊 Data Visualization
- • Pie charts with 3D perspective
- • Color mapping and gradients
- • Interactive viewports
Code Sample: Drawing a Cube
// Set up 3D view
glTranslatef(0.0, 0.0, -5.0);
glRotatef(30, 1.f, 1.f, 0.f);
// Draw cube faces with colors
glBegin(GL_QUADS);
// Front face - Green
glColor3f(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
glVertex3f(-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f);
glVertex3f( 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f);
glVertex3f( 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f);
glVertex3f(-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f);
// ... more faces
glEnd();Mathematical Curves
Curves generated using polar coordinate equations:
Limacon: r = a·cos(θ) + b
Cardioid: r = a·(1 + cos(θ))
Three-Leaf: r = a·cos(3θ)
Four-Leaf: r = a·cos(2θ)
Spiral: r = a·θ
Tech Stack
C++
OpenGL
GLUT
GLU
Linear Algebra
What I Learned
- • The graphics pipeline: vertex → transformation → rasterization → fragment
- • Matrix math for 3D transformations (translate, rotate, scale, project)
- • How GPUs use parallel processing for rendering
- • Double buffering to prevent screen tearing
- • Depth testing to handle occlusion in 3D scenes