Scaling Inference Time Compute for Machine Learning Engineering Agents
June 2025 — AIMS South Africa (AI for Science Program)
Abstract
Recent findings suggest that reasoning strategies applied during inference can bring greater performance gains in LLMs than simply increasing model size. In this work, we systematically implement and evaluate inference-time scaling (ITS) strategies within an open-source, agentic framework tailored to machine-learning engineering tasks.
We enhance the AIDE agent scaffold with multiple ITS techniques—self-consistency, self-reflection, and modular task decomposition—and apply these to distilled DeepSeek-R1 models (7B, 14B, 32B). Our best agent achieves a 30% medal rate on MLE-Bench, matching OpenAI's o4-mini and surpassing GPT-4-Turbo.
DeepSeek-32B + Decomposed Planner-Coder
Matches o4-mini • Surpasses GPT-4-Turbo
Research Questions
To what extent can ITS strategies improve the performance of distilled DeepSeek models on ML engineering tasks?
What are the performance trade-offs between different ITS strategies (self-consistency, self-reflection, task decomposition)?
Methodology
🤖 Models Tested
- • DeepSeek-R1 7B (distilled)
- • DeepSeek-R1 14B (distilled)
- • DeepSeek-R1 32B (distilled)
- Baselines: GPT-4-Turbo, o4-mini
📊 Benchmark
- • MLE-Bench (10 competitions)
- • Image/Text Classification
- • Tabular, Seq2Seq, Audio tasks
- • Pass@6 evaluation protocol
ITS Strategies Implemented
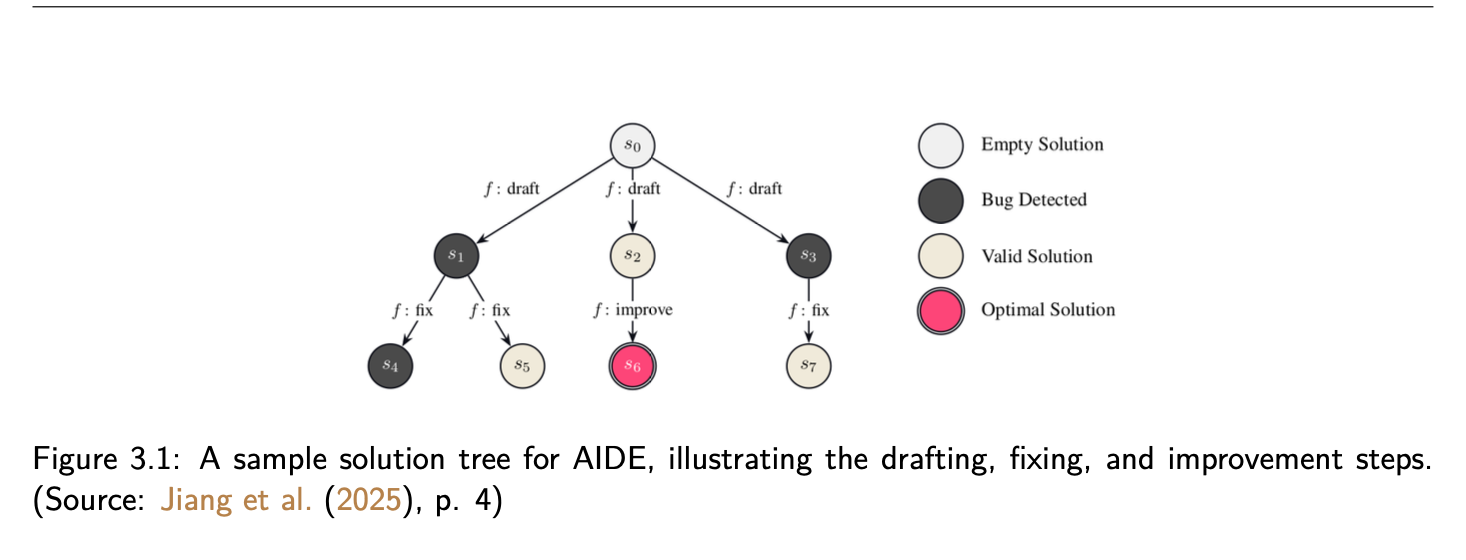
Figure 3.1: AIDE solution tree - drafting, fixing, and improvement steps
Self-Reflection
Iterative refinement based on execution feedback. Best for "competent but flawed" models.
Self-Consistency
Generate N candidates, verify and select best. Increases reliability.
Task Decomposition
Separate Planner + Coder agents. Most effective for 32B.
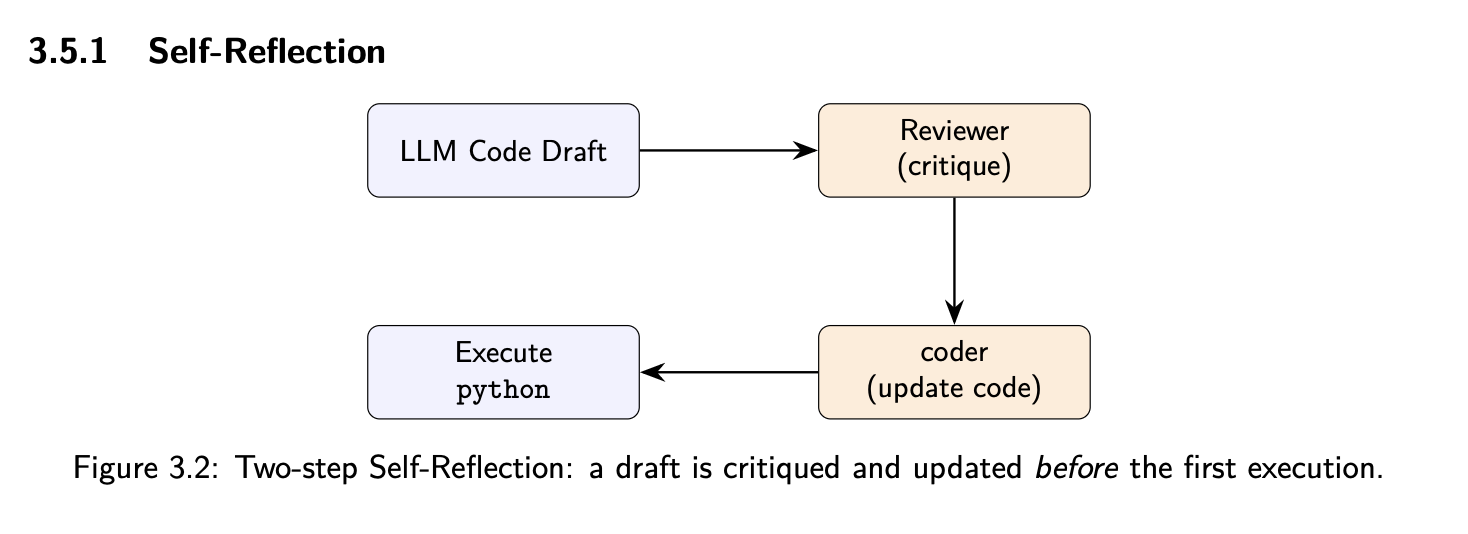
Figure 3.2: Self-Reflection workflow
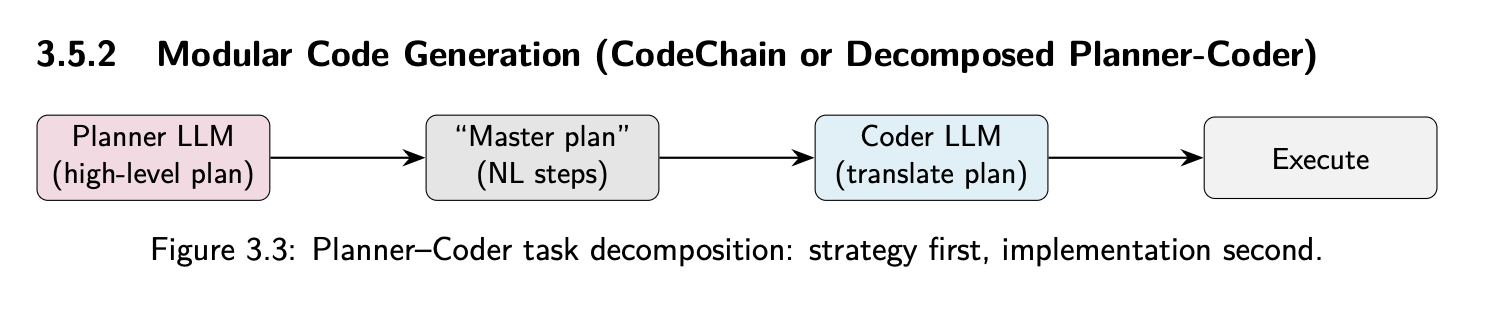
Figure 3.3: Planner-Coder decomposition
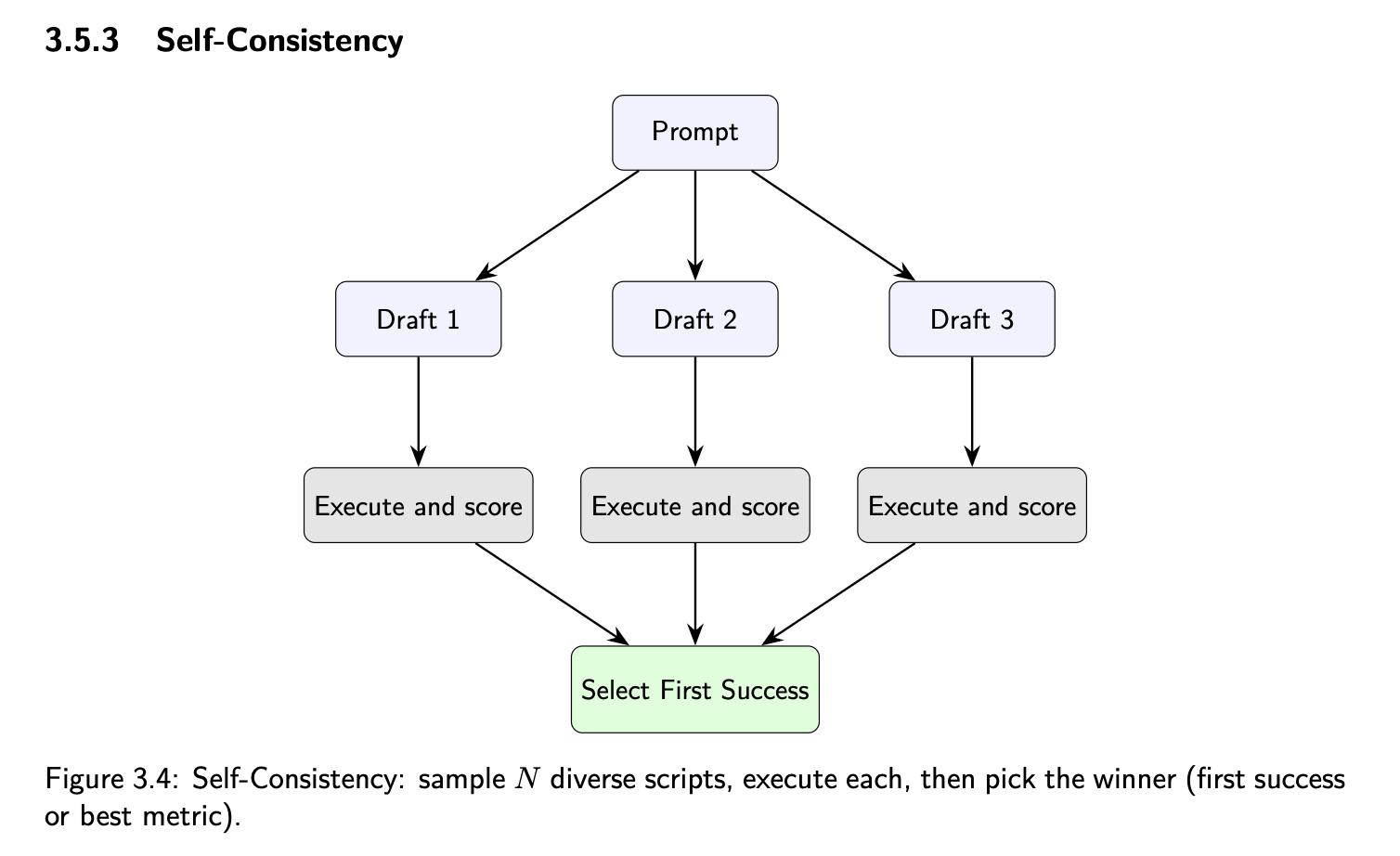
Figure 3.4: Self-Consistency - sample N scripts, execute, pick winner
Key Results
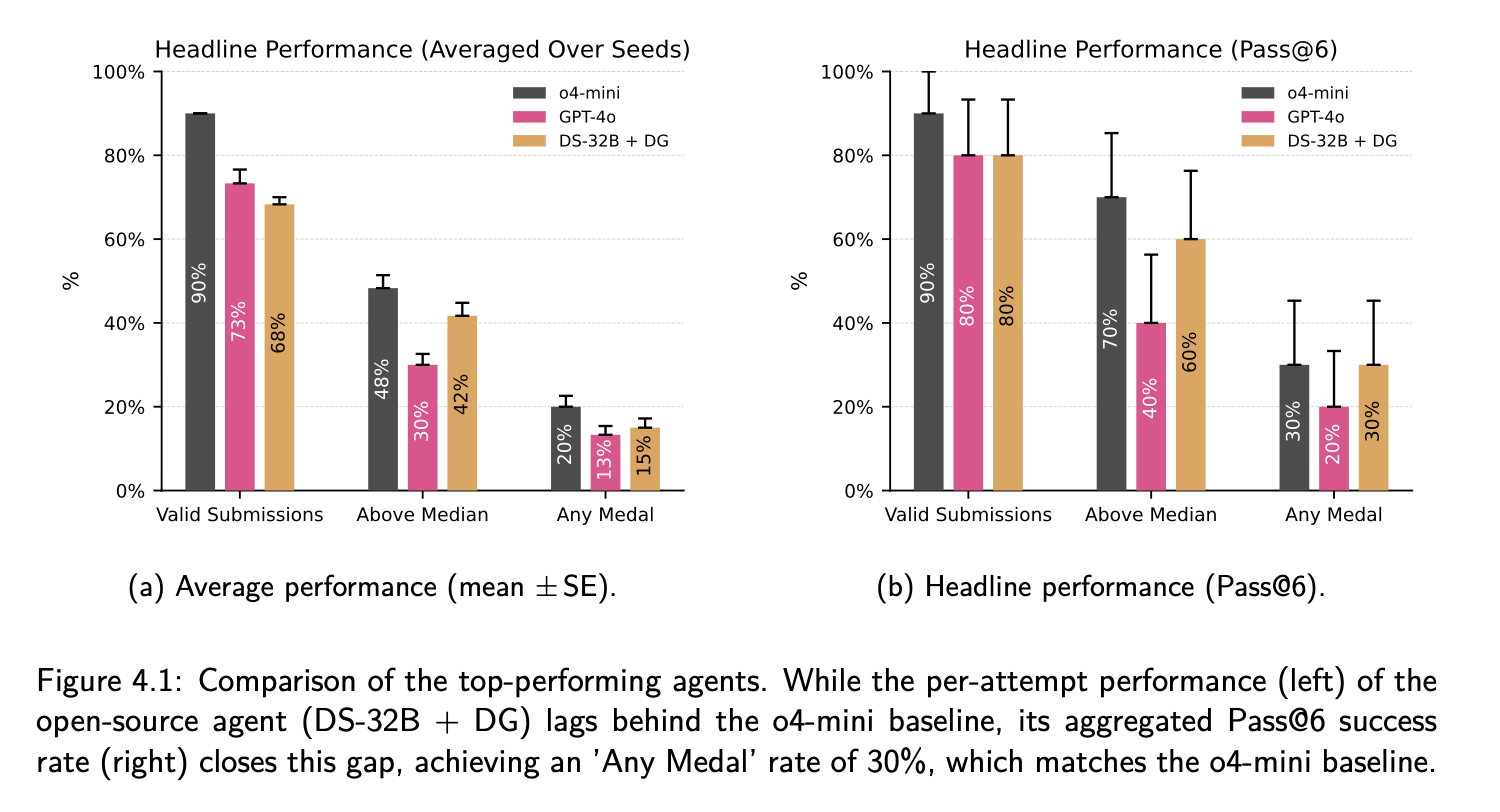
Figure 4.1: Comparison of top-performing agents. DS-32B + Decomposed achieves 30% medal rate (Pass@6), matching o4-mini.
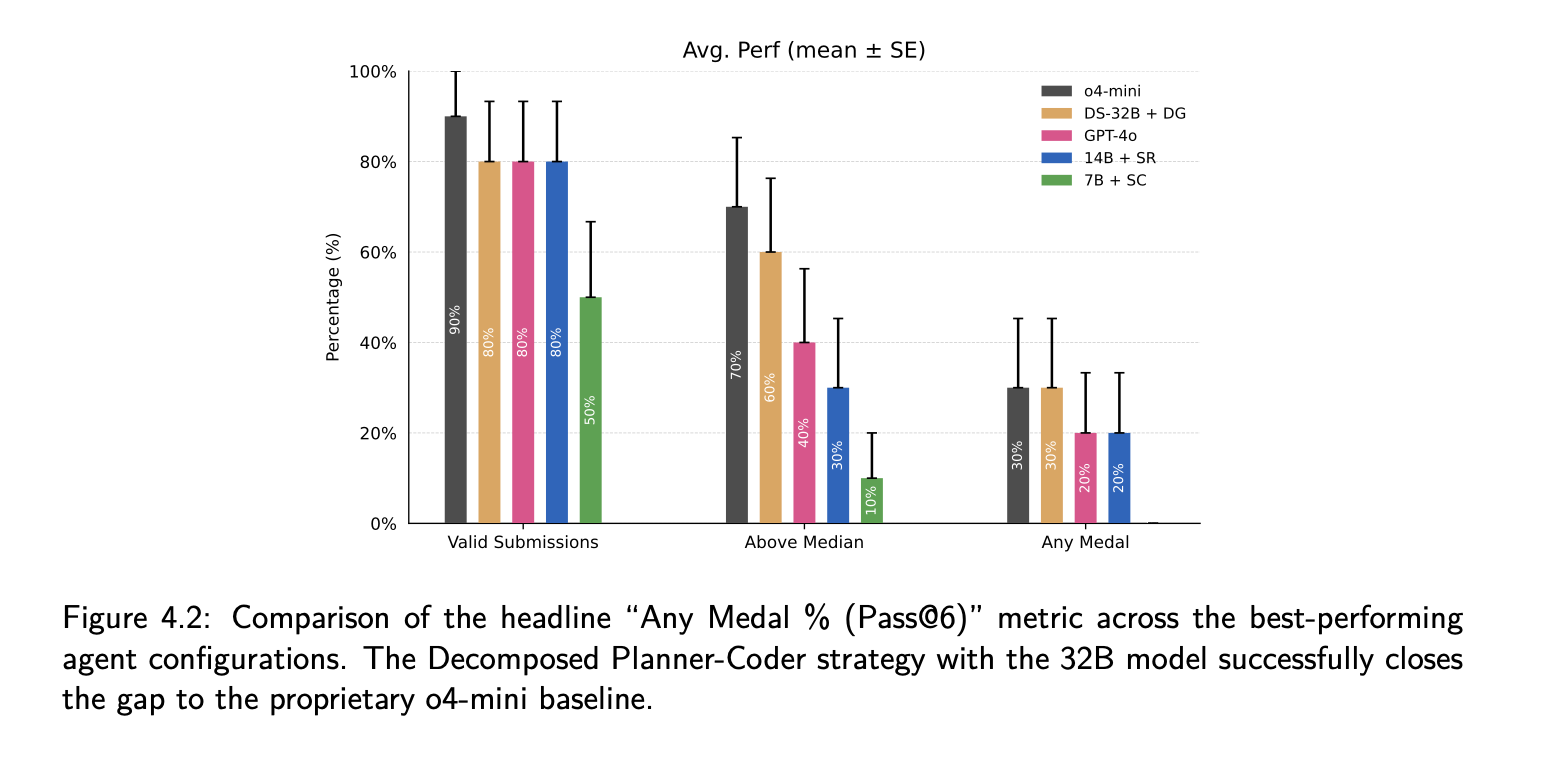
Figure 4.2: Any Medal % (Pass@6) across all configurations. Task decomposition provides the biggest gains for the 32B model.
| Model + Strategy | Valid Submission | Above Median | Any Medal |
|---|---|---|---|
| o4-mini (baseline) | 90% | 70% | 30% |
| GPT-4-Turbo (baseline) | 80% | 40% | 20% |
| 🏆 DS-32B + Decomposed | 80% | 60% | 30% |
| DS-32B + Self-Consistency | 80% | 50% | 10% |
| DS-14B + Self-Reflection | 80% | 30% | 20% |
| DS-7B (all strategies) | 50% | 10% | 0% |
Pass@6 results on 10 MLE-Bench competitions
Key Findings
🚫 ITS Cannot Rescue Weak Models
The 7B model's fundamental code generation deficits meant no ITS strategy could produce medal-winning solutions. ITS amplifies capability—it doesn't create it.
🏆 Task Decomposition Wins for Capable Models
Planner-Coder separation enforces architectural coherence, avoiding library confusion. The 32B model with this strategy matches o4-mini.
🎯 Self-Reflection: Sweet Spot at 14B
Most effective for "competent but flawed" models. Doubled the 14B medal rate but caused "overthinking" in the already-capable 32B.
⚖️ No One-Size-Fits-All Strategy
The optimal ITS strategy depends on both model scale and task type. Strategy selection is a critical design decision.
Contributions
Open-Source Agent Scaffold
Accessible, specialized agentic framework optimized for ITS strategies in ML engineering tasks.
Empirical Validation
Comprehensive experiments showing ITS can elevate open-source LLMs to match proprietary SOTA.
Supervision
Supervisors: Arnol Fokam, Arnu Pretorius
Institutions: InstaDeep & Stellenbosch University, South Africa
Program: AI for Science Masters, AIMS South Africa (DeepMind Partnership)